1. RAID 5 Data Recovery FAQ
Q: What is the definition of a “RAID 5” volume?
A: “RAID 5” refers to a “Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) Disks” that have been established in a Level 5, or striped with parity, volume set. A RAID 5 volume is a combination of hard drives that are configured for data to be written across three (3) or more drives.
Q: What is “parity” or “parity data”?
A: In a RAID 5 configuration, additional data is written to the disk that should allow the volume to be rebuilt in the event that a single drive fails. In the event that a single drive does fail, the volume continues to operate in a “degraded” state (no fault tolerance). Once the failed drive is replaced with a new hard drive (of the same or higher capacity), the “parity data” is used to rebuild the contents of the failed drive on the new one.
Q: What the minimum drive requirements to create a RAID 5 volume?
A: RAID 5 volume sets require a minimum of at least three (3) hard drives (preferably of the same capacity) to create and maintain a RAID 5 volume. If one drive is of a lower capacity than the others, the RAID controller (whether hardware or software) will treat every hard drive in the array as though it were of the same lower capacity and will establish the volume accordingly.
Q: What are the differences between “hardware” and “software” RAID 5 configurations?
A: With a software-based RAID 5 volume, the hard disk drives use a standard drive contoller and a software utility provides the management of the drives in the volume. A RAID 5 volume that relies on hardware for management will have a physical controller (commonly built into the motherboard, but it can also be a stand-alone expansion card) that provides for the reading and writing of data across the hard drives in the volume.
Q: What are the advantages of RAID 5 volumes?
A: A RAID 5 volume provides faster data access and fault tolerance, or protection against one of the drives failing during use. With a RAID 5 disk volume, information is striped (or written) across all of the drives in the array along with parity data. If one of the hard drives in the array becomes corrupted, drops out of a ready state or otherwise fails, the remaining hard drives will continue to operate as a striped volume with no parity and with no loss of data. The failed drive can be replaced in the array with one of equal or larger capacity, and the data it contained will be automatically rebuilt using the parity data contained on the other drives. Establishing a RAID 5 volume requires 3 disk drives as a minimum requirement.
Q: What are the disadvantages of RAID 5 configurations?
A: There are several disadvantages. RAID 5 results in the loss of storage capacity equivalent to the capacity of one hard drive from the volume. For example, three 500GB hard drives added together comprise 1500GB (or roughly about 1.5 terabytes) of storage. If the three (3) 500GB drives were established as a RAID 0 (striped) configuration, total data storage would equal 1500GB capacity . If these same three (3) drives are configured as a RAID 5 volume (striped with parity), the usable data storage capacity would be 1000GB and not 1500GB, since 500GB (the equivalent of one drives’ capacity) would be utilized for parity. In addition, if two (2) or more drives fail or become corrupted at the same
time, all data on the volume would be inaccessible to the user.
Q: Can data be recovered from a re-formatted RAID 5 volume?
A: Many times information is still recoverable, depending on how the drives were re-formatted. Re-formatting a volume using Windows, for example, will create what will appear to be a new “clean” volume – but the original data will still be on the disk in the “free and available” space. However, a low-level format (usually performed through an on-board RAID controller utility) will “wipe” or overwrite every single block on a drive. Unlike an O/S (or “high-level”) format, a low-level format normally is slower, takes a considerable amount of time and destroys the original data.
Q: Can I run recovery software utilities to recover my RAID volume data?
A: The safest approach to data recovery with a RAID volume (or with any media) is to capture every storage block on each device individually. The resulting drive “images” are then used to help rebuild the original array structure and recover the necessary files and folders. This approach limits continued interaction with the media and helps to preserve the integrity of the original device. One of the dangers in using data recovery software is that it forces the read / write heads to travel repeatedly over areas of the original media which, if physically damaged, could become further damaged and possibly unrecoverable.
Q: If a RAID 5 volume will not mount, should I allow a “rebuild” to run?
A: If one drive fails in a RAID 5 configuration, the volume still operates – but in a degraded state (it no longer writes parity information). The important data should be backed up immediately and verified to be usable before any rebuild operation is started. When it comes to critical data, anything that is used to read or write to the original volume represents a risk. Is the hardware operating properly? Are all other drives in the volume functioning correctly? If you are the least bit unsure, a rebuild should not be performed.
Q: If multiple drives fail in a RAID volume all at once, is the data still recoverable?
A: In many cases, the answer is yes. It usually requires that data be recovered from each failed hard drive individually before attempting to address the rest of the volume. The quality and integrity of the data recovered will depend on the extent of the damage incurred to each failed storage device.
2. How Raid 5 Data Recovery?
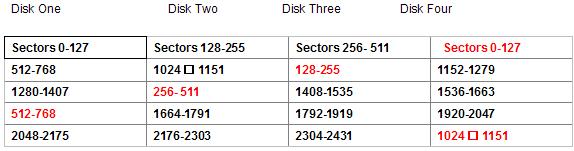
RAID 5 is a very popular RAID level that uses block level striping and distributed parity. This level tries to remove the bottleneck of the dedicated parity drive. With the use of a distributed parity algorithm, this level writes the data and parity data across all the drives. Basically, the blocks of data are used to create the parity blocks which are then stored across the array. This removes the bottleneck of writing to just one parity drive. However, the parity information still has to be written on a separate disk whenever a write occurs, so the slowdown involved with that still applies. There is also a small calculation that must take place for every write. The fault tolerance is maintained by separating the parity information for a block from the actual data block. This way when one drive fails, the array goes into degraded mode and begins reading and writing to the parity areas on the other disks in place of that bad drive. When a new disk is placed back into the RAID, the controller or software begins copying the parity data back to the new drive until complete, then the array will kick out of degraded mode. Recovery is more complicated than usual because of the distributed nature of the parity. Many RAID cards and software use separate and sometimes proprietary algorithms to generate the parity stripes. On illustration A you see just one example of RAID 5, generally referred to as standard or straight RAID 5. Many times you can get the striping pattern from the RAID card or software manufacturer.

As you can see in the illustration above, there is a clear pattern. The sectors in the virtual disk are striped evenly across the disks, but every fourth stripe is dedicated to parity. Red denotes parity data.
Controller Requirements: Supported by most hardware controllers, both SCSI and IDE/ATA, and also most software RAID solutions.
Hard Disk Requirements: Minimum of three hard. Any type may be used, but they should be of identical type and size for best performance and to eliminate “waste”.
Array Capacity: (Size of Smallest Drive * Number of Drives Smallest Drive).
Fault Tolerance: Any one drive may fail and the array continues to operate (in fact, it operates faster in degraded mode!) Failure of another drive results in loss of all data, which is why you paid the big bucks!
Storage Efficiency: 75% if identical drives are used.
Availability: Loss of one disk = continued server functionality.
Rebuilding (Scrubbing) and Degradation: Rebuilding takes place automatically with most RAID cards and software.
Random Read Performance: Excellent
Random Write Performance: Moderate
Sequential Read Performance: Moderate
Sequential Write Performance: Very good.
RAID 5 uses a distributed parity algorithm, this level writes the data and parity data across all the drives. The blocks of data are used to create the parity blocks which are then stored across the array. Block size can be anything, but is typically 64kB (128 sectors) Disk 0 will contain the first sector 0 through 127, disk 1 will contain sectors 128 through 255, and this will continue to alternate until you reach the last disk of the set, and this disk will be the parity disk. The parity disk will rotate based on the parity rotation algorithm for that particular RAID card or software. One complication can be expected in some cases, and that is the presence of an offset. An offset is a number of sectors before the first striped block. The presence of an offset is common in Adaptec cards. The offset can easily be found by searching for the partition table. When found, simply take the sector number where the partition table is located, and clone the disk to a file starting with this sector. Repeat on all drives and you have a starting point!
The next step is to find the stripe size. This is a very critical step and you must be absolutely sure. Typically the stripe size will be the same as the default setting for the card that was used. For instance, a Dell PERC 2 adaptec RAID card has a stripe size of 32K (64 sectors) and an offset of 64K (128 sectors). Use this as your starting point if possible. If you do not know the card type used, it is wise to use 64K (128 sectors) as your starting point as this is most common among all cards.
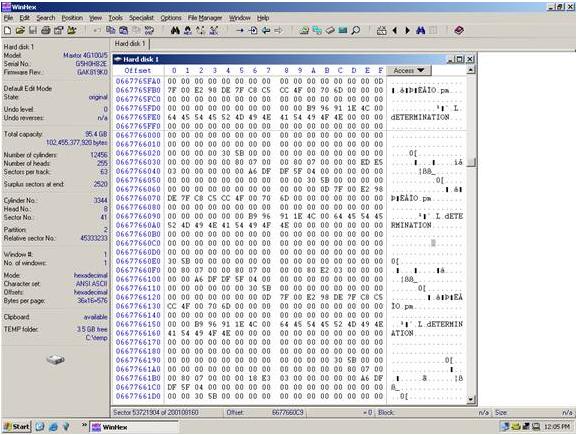
Now use Winhex to find a location on the disk that is easy to see a pattern. See the example below. Notice how we have text, apparently from a database of some sort. This text can be used to identify a data pattern. Now look at the current sector (53,721,904). Divide this number by the suspected stripe size in sectors. In this case the stripe size we are attempting to validate is 128 sectors. The resulting number will probably not be a whole number. In this case it is 419702.375. Take the whole number of 419702 and multiply this by the suspected stripe size (128). The resulting number is what we will refer to as the stripe break point. It is necessary to know this simple calculation for all types of RAID except RAID 1 (mirroring).
Find the break point:
53721904/128=419702.375419702*128 = 53721856
Answer: A break point is located at sector 53, 721, 856

Notice above how we have text, apparently from a database of some sort. This text can be used to identify a data pattern.

Notice how at the exact break point of 53, 721, 856 we have a definite difference of data. This is because the stripe is from a separate area of the volume. Not all break points will be this easy. In some cases you will have to look at the actual data and determine if consistency exists. Train your eyes to catch a break point while you are scrolling the sectors using the page down function, and you will become very proficient. You will often have to repeat the steps above on different areas of the disk if the data is too inconsistent to determine the break point.
Once the break point is discovered, you will then be able to start the RAID 5 de-striping process.
The best starting point is to clone all disks twice (to be sure) into image files on separate disks. Obtain the original card or find out the card make and model and purchase this.
Assuming you have no idea where the disks belong in the RAID then you must find a point on the disk where the data is sequential. This is very difficult unless the volume is formatted with NTFS, FAT32, or FAT16. In this case, you can use the Master boot record and NTFS/FAT32/FAT16 boot record to find the location of the MFT files or FAT tables.
RAID-5 Parity Rotation
RAID-5 under any operating system can use one of four algorithms for the placement of segments among the disks in the array. -Keep in mind in your troubleshooting that there may be an offset throwing everything off. Find the partition table or OS identifier and us this as your definite sector 0. In a RAID 5 there should be two drives with a partition table. One is the first drive in that array and one is the last drive in the array.
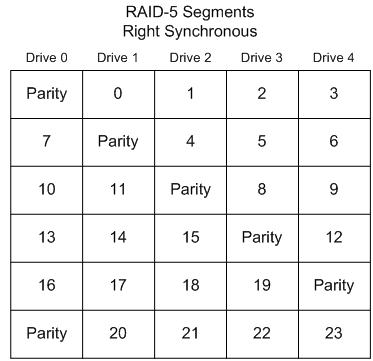
Right Synchronous
Left Synchronous,
Left Asynchronous
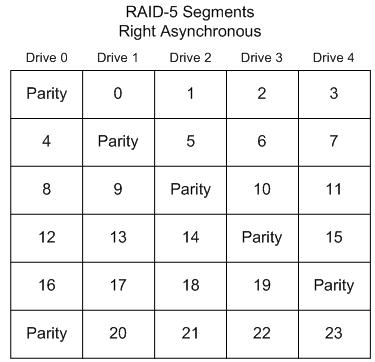
Right Asynchronous
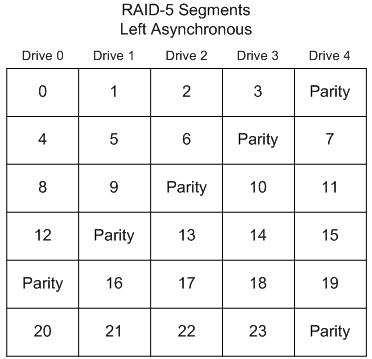
Left Asynchronous (Backwards Parity Rotation, Standard)
In this layout, the segments are numbered sequentially, starting with the first non-parity drive in the stripe. The parity drive starts at the last drive, and moves backwards one drive per stripe. While this is the hardware ‘standard’ RAID-5 layout, it is not the default for Linux or Windows 2000, 2003 Server. This is sometimes called backwards parity or standard Rotation R-studio supports this mode.

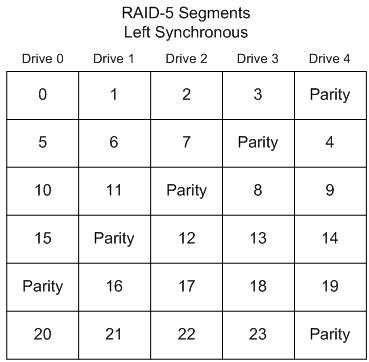
Left Synchronous
In this layout, the segments are numbered sequentially, starting with the first drive in the stripe after the parity. The segments wrap. The parity drive starts at the left-most drive, and moves right one drive per stripe. This is the default RAID-5 segment layout under Linux.
For large reads, this segment layout is the fastest. This is because each consecutive group of segments that is no larger than the total number of disks in the array, will use all the disks in the array.
Right Asynchronous (Forward Parity Rotation)
In this layout, the segments are numbered sequentially, starting with the first non-parity drive in the stripe. The parity drive starts at the right-most drive, and moves left one drive per stripe.

Right Synchronous
In this layout, the segments are numbered sequentially, starting with the first drive in the stripe after the parity. The segments wrap. The parity drive starts at the right-most drive, and moves left one drive per stripe.

Refer to the partition and boot sector repair section of this manual if the disk is not mountable, or review the stripe break points.
Recommended RAID 5 Recovery Software: Getway Raid Recovery Software





 1. Why RAID data recovery?
1. Why RAID data recovery?