 1. RAID 0 Data Recovery FAQ:
1. RAID 0 Data Recovery FAQ:
Q: What is a “RAID 0” configuration?
A: A RAID 0 (zero) volume set is a group of hard disk drives that are combined and accessed together based on a pre-defined configuration to allow for “data striping” across multiple drives. The term “RAID” refers to a “Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) Disks”. RAID 0 drive sets are also described as “striped without parity” and “non-redundant” volumes.
Q: What is meant by the term “disk striping”?
A: Within a disk striping (RAID 0) volume, information will be written evenly , or “striped”, over at least 2 (if not more) disk drives.
Q: How many drives are needed for a RAID 0 volume?
A: To establish a RAID 0 volume, a minimum of at least 2 hard disk drives ar required. Unlike RAID 1, the number of drives used in the array can be an odd or even number.
Q: What is the difference between “hardware” and “software” RAID 0 configurations?
A: Hardware-based RAID 0 uses a physical controller (either as a separate plug-in board or as part of the motherboard) that provides for the striping of data across the drives in the volume. With a software-based RAID 0 volume, the drives are attached to a normal drive contoller and software controls the order and writing to drives in the volume set.
Q: What are the benefits of using drives set up as a RAID 0?
A: A RAID 0 (disk striping) set will use the maximum amount of available storage capacity of each drive in the array, and allows for faster access and retrieval of data.
Q: What are the negatives associated with RAID 0?
A: RAID 0 (disk striping) does not provide any protection against drive failures. If one or more drives fail, all of the information contained on the volume becomes totally inaccessable. On the other hand, with a mirrored disk volume (RAID 1), information is written to the first drive and then to a second (or “mirror”) drive at the same time. If one of the hard drives in the mirror volume fails, the remaining hard drive can be placed in service as a single drive with no loss of information. Similar to a RAID 0 volume, RAID 1 volumes require a minimum of two (2) drives.
Q: Can RAID 0 be combined with another type of RAID, like RAID 1?
A: The combination of striping and then mirroring is referred to as RAID 0+1. In this scenario, the configuration will provide disk striping (RAID 0) across 2 or more drives and will “mirror” the data in real-time to a duplicate drive set (RAID 1). This unique combination will provide fault tolerance, but it does so at the expense of usable storage space. A volume established as a RAID 0+1 volume will need four (4) hard drives at a minimum to be configured.
Q: Can data be recovered from a re-formatted RAID 0 volume?
A: Many times information is still recoverable, depending on how the drives were re-formatted. Re-formatting a volume using Windows, for example, will create what will appear to be a new “clean” volume – but the original data will still be on the disk in the “free and available” space. A low-level format to “wipe” or overwrite every single block takes a considerable amount of time and destroys the original data.
Q: Could data recovery software utilities be used to recover my RAID 0?
A: Perhaps, but it wouldn’t be the safest approach. Most data recovery software will require the read / write heads to constantly travel over areas of the original disk that, if there is any physical damage, could render the surfaces useless and beyond recovery. The safest method of recovering data from a failed or corrupted RAID 0 volume (or with any storage device) is to create a block-level copy of every sector on each hard drive. The copied image is then used to reconstruct the original volume and rescue the required files and directories. This approach, while more time consuming, maintains and preserves the data integrity of the drive media and limits the number of times that the original drive needs to be accessed. It also protects against any writing to the original media, which could result in an inadvertent overwrite of the data that needs to be recovered.
Q: With RAID 0, if one or more drives become corrupted or fail, is data recoverable?
A: In most situations, data will be recoverable. The quality and integrity of the data recovered will depend on the extent of the damage incurred to each failed storage device. The drives will need to be addressed and recovered individually before attempting to address the set as a volume.
2. How Raid 0 Data Recovery?
Use at your own risk, and always make backups of your disks before performing any data recovery procedure.
RAID 0 is simply blocks of data striped between two disks. Block size can be anything, but is typically 64kB (128 sectors) Disk 0 will contain the first sector 0 through 127, disk 1 will contain sectors 128 through 255, and this will continue to alternate throughout the entire virtual disk. One complication can be expected in some cases, and that is the presence of an offset. An offset is a number of sectors before the first striped block. The presence of an offset is common in Adaptec cards. The offset can easily be found by searching for the partition table. When found, simply take the sector number where the partition table is located, and clone the disk to a file starting with this sector.
The next step is to find the stripe size. This is a very critical step and you must be absolutely sure. Typically the stripe size will be the same as the default setting for the card that was used. For instance, a Dell PERC 2 adaptec RAID card has a stripe size of 32K (64 sectors) and an offset of 64K (128 sectors). Use this as your starting point if possible. If you do not know the card type used, it is wise to use 64K (128 sectors) as your starting point as this is most common among all cards.
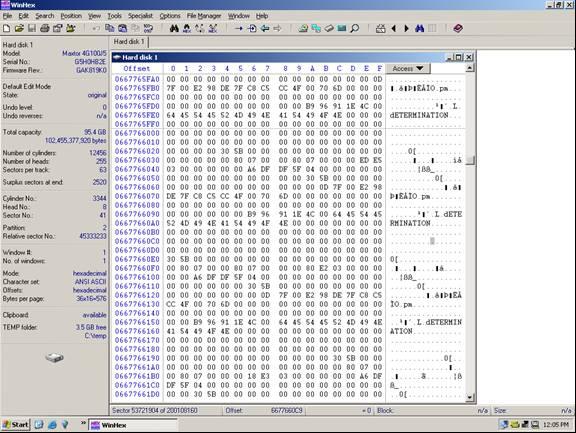
Now use Winhex to find a location on the disk that is easy to see a pattern. See the example below.

Notice above how we have text, apparently from a database of some sort. This text can be used to identify a data pattern. Now look at the current sector (53,721,904). Divide this number by the suspected stripe size in sectors. In this case the stripe size we are attempting to validate is 128 sectors. The resulting number will probably not be a whole number. In this case it is 419702.375. Take the whole number of 419702 and multiply this by the suspected stripe size (128). The resulting number is what we will refer to as the stripe break point. It is necessary to know this simple calculation for all types of RAID except RAID 1 (mirroring).
Find the break point:
53721904/128=419702.375
419702*128 = 53721856
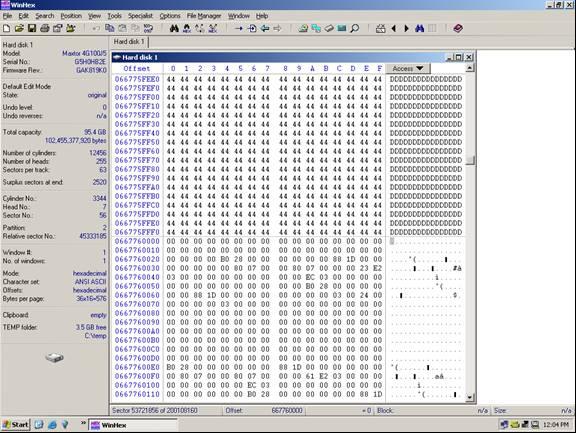
Answer: A break point is located at sector 53, 721, 856 (see illustration below)

Notice how at the exact break point of 53, 721, 856 we have a definite difference of data. This is because the stripe is from a separate area of the volume. Not all break points will be this easy. In some cases you will have to look at the actual data and determine if consistency exists. Train your eyes to catch a break point while you are scrolling the sectors using the page down function, and you will become very proficient. You will often have to repeat the steps above on different areas of the disk if the data is too inconsistent to determine the break point.
Once the break point is discovered, you will then be able to start the de-striping process. Using a software utility, such as the hex editor Winhex, place the disk images in the proper order, adjust the stripe size, and clone to a hard disk. Once complete, the disk should be mountable. Refer to the partition and boot sector repair section of this manual if the disk is not mountable, or review the stripe break points.



 A USB flash drive is a NAND type flash memory. The NAND type flash memory was designed for the exchange and saving of data as alternative to the magnetic disk. The NAND type flash memory has the capacity to hold large volumes of data. The writing and erasing speed is also fast. The USB drive can be easily inserted into the USB port of the computer. With the help of USB flash drive, data can be safely and easily transferred. The USB drive is more reliable and safer than the floppy disks. The USB drives are small and compact.
A USB flash drive is a NAND type flash memory. The NAND type flash memory was designed for the exchange and saving of data as alternative to the magnetic disk. The NAND type flash memory has the capacity to hold large volumes of data. The writing and erasing speed is also fast. The USB drive can be easily inserted into the USB port of the computer. With the help of USB flash drive, data can be safely and easily transferred. The USB drive is more reliable and safer than the floppy disks. The USB drives are small and compact. The external hard drives can be portable and connects to the computer system from external. Cable is used for connecting the external hard drives to computer system; it supports the IDE, SCSI and USB. The other bus standards are also compatible. For windows operating system, the internal hard drives were used in the computer systems during the last years of the twentieth century. On the other hand the external drives were mostly used on Apple Macintosh during the twentieth century.
The external hard drives can be portable and connects to the computer system from external. Cable is used for connecting the external hard drives to computer system; it supports the IDE, SCSI and USB. The other bus standards are also compatible. For windows operating system, the internal hard drives were used in the computer systems during the last years of the twentieth century. On the other hand the external drives were mostly used on Apple Macintosh during the twentieth century.
 The SD memory cards known as the “Secure Digital” first began as miniature cards. Afterwards the new and advanced form of the SD memory card SDIO “Secure Digital Input/output” was introduced into the market. The SDA “Secure Digital Association” included new features and technology to the SD memory cards. The SDA included new varieties of card functions. These new card functions included wireless “Local Area Network LAN” devices, cell phones, GPS receiver, digital video camera etc. The memory card readers that were used in the Secure Digital devices connected to the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The Windows Operating System detects and manages the SD (Secure Digital) memory cards through the driver called the (USB) Universal Serial Bus mass storage. The (SD) Secure Digital host controllers are supported by the Operating System. The Operating System connects the host controller SD to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. When the SD-host controller is detected by the operating system, the “SD Secure Digital bus driver” is loaded by the operating system OS. When the SD card is inserted by the user, the windows Operating system loads two drivers the “Storage mini-port” and the “SD Secure Digital Storage Class”. These two drivers are loaded on top of “Bus driver” by the Windows Operating System. On the other hand if the SD memory card of a different function like the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) or the Global Positioning System is inserted by the user, then the Windows Operating System loads the driver that is supplied by the vendor. It is necessary that both the vendor supplied and the native drivers in the (SD) Secure Digital stack communicate with “Secure Digital Bus”. The device drivers call the routines to communication with the “Secure Digital Bus”. These routines are called in the static “Secure Digital Bus library”. When the SD Secure Digital drivers compile, it is necessary that they link to the “Secure Digital SD Bus library”. There are some limitations for the SD device drivers. The “Host Controller Register” is not directly accessible by the Secure Digital device drivers.
The SD memory cards known as the “Secure Digital” first began as miniature cards. Afterwards the new and advanced form of the SD memory card SDIO “Secure Digital Input/output” was introduced into the market. The SDA “Secure Digital Association” included new features and technology to the SD memory cards. The SDA included new varieties of card functions. These new card functions included wireless “Local Area Network LAN” devices, cell phones, GPS receiver, digital video camera etc. The memory card readers that were used in the Secure Digital devices connected to the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The Windows Operating System detects and manages the SD (Secure Digital) memory cards through the driver called the (USB) Universal Serial Bus mass storage. The (SD) Secure Digital host controllers are supported by the Operating System. The Operating System connects the host controller SD to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. When the SD-host controller is detected by the operating system, the “SD Secure Digital bus driver” is loaded by the operating system OS. When the SD card is inserted by the user, the windows Operating system loads two drivers the “Storage mini-port” and the “SD Secure Digital Storage Class”. These two drivers are loaded on top of “Bus driver” by the Windows Operating System. On the other hand if the SD memory card of a different function like the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) or the Global Positioning System is inserted by the user, then the Windows Operating System loads the driver that is supplied by the vendor. It is necessary that both the vendor supplied and the native drivers in the (SD) Secure Digital stack communicate with “Secure Digital Bus”. The device drivers call the routines to communication with the “Secure Digital Bus”. These routines are called in the static “Secure Digital Bus library”. When the SD Secure Digital drivers compile, it is necessary that they link to the “Secure Digital SD Bus library”. There are some limitations for the SD device drivers. The “Host Controller Register” is not directly accessible by the Secure Digital device drivers.