Magnetic storage is essentially an analog medium. The data a PC stores on it, however, is digital information that is, 1s and 0s. When the drive sends digital information to a magnetic recording head, the head creates magnetic domains on the storage medium with specific polarities corresponding to the positive and negative voltages the drive applies to the head. The flux reversals form the boundaries between the areas of positive and negative polarity that the drive controller uses to encode the digital data onto the analog medium. During a read operation, each flux reversal the drive detects generates a positive or negative pulse that the device uses to reconstruct the original binary data.
To optimize the placement of flux transitions during magnetic storage, the drive passes the raw digital input data through a device called an encoder/decoder (endec), which converts the raw binary information to a waveform designed to optimally place the flux transitions (pulses) on the media. During a read operation, the endec reverses the process and decodes the pulse train back into the original binary data. Over the years, several schemes for encoding data in this manner have been developed; some are better or more efficient than others, which you see later in this section.
Other descriptions of the data encoding process might be much simpler, but they omit the facts that make some of the issues related to hard drive reliability so critical namely, timing. Engineers and designers are constantly pushing the envelope to stuff more and more bits of information into the limited quantity of magnetic flux reversals per inch. What they’ve come up with, essentially, is a design in which the bits of information are decoded not only from the presence or absence of flux reversals, but from the timing between them. The more accurately they can time the reversals, the more information that can be encoded (and subsequently decoded) from that timing information.
In any form of binary signaling, the use of timing is significant. When interpreting a read or write waveform, the timing of each voltage transition event is critical. Timing is what defines a particular bit or transition cell that is, the time window within which the drive is either writing or reading a transition. If the timing is off, a given voltage transition might be recognized at the wrong time as being in a different cell, which would throw the conversion or encoding off, resulting in bits being missed, added, or misinterpreted. To ensure that the timing is precise, the transmitting and receiving devices must be in perfect synchronization. For example, if recording a 0 is done by placing no transition on the disk for a given time period or cell, imagine recording ten 0 bits in a row you would have a long period of ten time periods or cells with no transitions.
Imagine now that the clock on the encoder was slightly off time while reading data as compared to when it was originally written. If it were fast, the encoder might think that during this long stretch of 10 cells with no transitions, only 9 cells had actually elapsed. Or if it were slow, it might think that 11 cells had elapsed instead. In either case, this would result in a read error, meaning the bits that were originally written would not be read as being the same. To prevent timing errors in drive encoding/decoding, perfect synchronization is necessary between the reading and writing processes. This synchronization often is accomplished by adding a separate timing signal, called a clock signal, to the transmission between the two devices. The clock and data signals also can be combined and transmitted as a single signal. Most magnetic data encoding schemes use this type of combination of clock and data signals.
Adding a clock signal to the data ensures that the communicating devices can accurately interpret the individual bit cells. Each bit cell is bounded by two other cells containing the clock transitions. By sending clock information along with the data, the clocks remain in sync, even if the medium contains a long string of identical 0 bits. Unfortunately, the transition cells used solely for timing take up space on the medium that could otherwise be used for data.
Because the number of flux transitions a drive can record in a given space on a particular medium is limited by the physical nature or density of the medium and the head technology, drive engineers have developed various ways of encoding the data by using a minimum number of flux reversals (taking into consideration the fact that some flux reversals used solely for clocking are required). Signal encoding enables the system to make the maximum use of a given drive hardware technology.
Although various encoding schemes have been tried, only a few are popular today. Over the years, these three basic types have been the most popular:
- Modified Frequency Modulation
FM Encoding
One of the earliest techniques for encoding data for magnetic storage is called Frequency Modulation encoding. This encoding schemesometimes called Single-Density encodingwas used in the earliest floppy disk drives installed in PC systems. The original Osborne portable computer, for example, used these Single-Density floppy disk drives, which stored about 80KB of data on a single disk. Although it was popular until the late 1970s, FM encoding is no longer used.
MFM Encoding
Modified Frequency Modulation encoding was devised to reduce the number of flux reversals used in the original FM encoding scheme and, therefore, to pack more data onto the disk. MFM encoding minimizes the use of clock transitions, leaving more room for the data. It records clock transitions only when a stored 0 bit is preceded by another 0 bit; in all other cases, a clock transition is not required. Because MFM minimizes the use of clock transitions, it can double the clock frequency used by FM encoding, enabling it to store twice as many data bits in the same number of flux transitions.
Because MFM encoding writes twice as many data bits by using the same number of flux reversals as FM, the clock speed of the data is doubled and the drive actually sees the same number of total flux reversals as with FM. This means a drive using MFM encoding reads and writes data at twice the speed of FM, even though the drive sees the flux reversals arriving at the same frequency as in FM.
Because it is twice as efficient as FM encoding, MFM encoding also has been called Double-Density recording. MFM is used in virtually all PC floppy disk drives today and was used in nearly all PC hard disks for a number of years. Today, virtually all hard disks use variations of RLL encoding, which provides even greater efficiency than MFM.

RLL Encoding
Today’s most popular encoding scheme for hard disks, called Run Length Limited, packs up to twice the information on a given disk than MFM does and three times as much information as FM. In RLL encoding, the drive combines groups of bits into a unit to generate specific patterns of flux reversals. By combining the clock and data signals in these patterns, the clock rate can be further increased while maintaining the same basic distance between the flux transitions on the storage medium.
IBM invented RLL encoding and first used the method in many of its mainframe disk drives. During the late 1980s, the PC hard disk industry began using RLL encoding schemes to increase the storage capabilities of PC hard disks. Today, virtually every drive on the market uses some form of RLL encoding.
Instead of encoding a single bit, RLL typically encodes a group of data bits at a time. The term Run Length Limited is derived from the two primary specifications of these codes, which are the minimum number (the run length) and maximum number (the run limit) of transition cells allowed between two actual flux transitions. Several variations of the scheme are achieved by changing the length and limit parameters, but only two have achieved any real popularity: RLL 2,7 and RLL 1,7.
You can even express FM and MFM encoding as a form of RLL. FM can be called RLL 0,1 because as few as zero and as many as one transition cells separate two flux transitions. MFM can be called RLL 1,3 because as few as one and as many as three transition cells separate two flux transitions. (Although these codes can be expressed as variations of RLL form, it is not common to do so.)
RLL 2,7 was initially the most popular RLL variation because it offers a high-density ratio with a transition detection window that is the same relative size as that in MFM. This method provides high storage density and fairly good reliability. In very high-capacity drives, however, RLL 2,7 did not prove to be reliable enough. Most of today’s highest capacity drives use RLL 1,7 encoding, which offers a density ratio 1.27 times that of MFM and a larger transition detection window relative to MFM. Because of the larger relative timing window or cell size within which a transition can be detected, RLL 1,7 is a more forgiving and more reliable code, which is important when media and head technology are being pushed to their limits.
Another little-used RLL variation called RLL 3,9sometimes also called Advanced RLL (ARLL)allows an even higher density ratio than RLL 2,7. Unfortunately, reliability suffered too greatly under the RLL 3,9 scheme; the method was used by only a few now-obsolete controllers and has all but disappeared.
Understanding how RLL codes work is difficult without looking at an example. Within a given RLL variation, such as RLL 2,7 or 1,7, you can construct many flux transition encoding tables to demonstrate how particular groups of bits are encoded into flux transitions.
In the conversion table, specific groups of data that are 2, 3, and 4 bits long are translated into strings of flux transitions 4, 6, and 8 transition cells long, respectively. The selected transitions for a particular bit sequence are designed to ensure that flux transitions do not occur too closely together or too far apart.

Limiting how close two flux transitions can be is necessary because of the fixed resolution capabilities of the head and storage medium. Limiting how far apart two flux transitions can be ensures that the clocks in the devices remain in sync.
You might think that encoding a byte value such as 00000001b would be impossible because no combinations of data bit groups fit this byte. Encoding this type of byte is not a problem, however, because the controller does not transmit individual bytes; instead, the controller sends whole sectors, making encoding such a byte possible by including some of the bits in the following byte. The only real problem occurs in the last byte of a sector if additional bits are necessary to complete the final group sequence. In these cases, the endec in the controller adds excess bits to the end of the last byte. These excess bits are then truncated during any reads so the controller always decodes the last byte correctly


 A USB flash drive is a NAND type flash memory. The NAND type flash memory was designed for the exchange and saving of data as alternative to the magnetic disk. The NAND type flash memory has the capacity to hold large volumes of data. The writing and erasing speed is also fast. The USB drive can be easily inserted into the USB port of the computer. With the help of USB flash drive, data can be safely and easily transferred. The USB drive is more reliable and safer than the floppy disks. The USB drives are small and compact.
A USB flash drive is a NAND type flash memory. The NAND type flash memory was designed for the exchange and saving of data as alternative to the magnetic disk. The NAND type flash memory has the capacity to hold large volumes of data. The writing and erasing speed is also fast. The USB drive can be easily inserted into the USB port of the computer. With the help of USB flash drive, data can be safely and easily transferred. The USB drive is more reliable and safer than the floppy disks. The USB drives are small and compact. The external hard drives can be portable and connects to the computer system from external. Cable is used for connecting the external hard drives to computer system; it supports the IDE, SCSI and USB. The other bus standards are also compatible. For windows operating system, the internal hard drives were used in the computer systems during the last years of the twentieth century. On the other hand the external drives were mostly used on Apple Macintosh during the twentieth century.
The external hard drives can be portable and connects to the computer system from external. Cable is used for connecting the external hard drives to computer system; it supports the IDE, SCSI and USB. The other bus standards are also compatible. For windows operating system, the internal hard drives were used in the computer systems during the last years of the twentieth century. On the other hand the external drives were mostly used on Apple Macintosh during the twentieth century.
 The SD memory cards known as the “Secure Digital” first began as miniature cards. Afterwards the new and advanced form of the SD memory card SDIO “Secure Digital Input/output” was introduced into the market. The SDA “Secure Digital Association” included new features and technology to the SD memory cards. The SDA included new varieties of card functions. These new card functions included wireless “Local Area Network LAN” devices, cell phones, GPS receiver, digital video camera etc. The memory card readers that were used in the Secure Digital devices connected to the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The Windows Operating System detects and manages the SD (Secure Digital) memory cards through the driver called the (USB) Universal Serial Bus mass storage. The (SD) Secure Digital host controllers are supported by the Operating System. The Operating System connects the host controller SD to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. When the SD-host controller is detected by the operating system, the “SD Secure Digital bus driver” is loaded by the operating system OS. When the SD card is inserted by the user, the windows Operating system loads two drivers the “Storage mini-port” and the “SD Secure Digital Storage Class”. These two drivers are loaded on top of “Bus driver” by the Windows Operating System. On the other hand if the SD memory card of a different function like the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) or the Global Positioning System is inserted by the user, then the Windows Operating System loads the driver that is supplied by the vendor. It is necessary that both the vendor supplied and the native drivers in the (SD) Secure Digital stack communicate with “Secure Digital Bus”. The device drivers call the routines to communication with the “Secure Digital Bus”. These routines are called in the static “Secure Digital Bus library”. When the SD Secure Digital drivers compile, it is necessary that they link to the “Secure Digital SD Bus library”. There are some limitations for the SD device drivers. The “Host Controller Register” is not directly accessible by the Secure Digital device drivers.
The SD memory cards known as the “Secure Digital” first began as miniature cards. Afterwards the new and advanced form of the SD memory card SDIO “Secure Digital Input/output” was introduced into the market. The SDA “Secure Digital Association” included new features and technology to the SD memory cards. The SDA included new varieties of card functions. These new card functions included wireless “Local Area Network LAN” devices, cell phones, GPS receiver, digital video camera etc. The memory card readers that were used in the Secure Digital devices connected to the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The Windows Operating System detects and manages the SD (Secure Digital) memory cards through the driver called the (USB) Universal Serial Bus mass storage. The (SD) Secure Digital host controllers are supported by the Operating System. The Operating System connects the host controller SD to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. When the SD-host controller is detected by the operating system, the “SD Secure Digital bus driver” is loaded by the operating system OS. When the SD card is inserted by the user, the windows Operating system loads two drivers the “Storage mini-port” and the “SD Secure Digital Storage Class”. These two drivers are loaded on top of “Bus driver” by the Windows Operating System. On the other hand if the SD memory card of a different function like the wireless Local Area Network (LAN) or the Global Positioning System is inserted by the user, then the Windows Operating System loads the driver that is supplied by the vendor. It is necessary that both the vendor supplied and the native drivers in the (SD) Secure Digital stack communicate with “Secure Digital Bus”. The device drivers call the routines to communication with the “Secure Digital Bus”. These routines are called in the static “Secure Digital Bus library”. When the SD Secure Digital drivers compile, it is necessary that they link to the “Secure Digital SD Bus library”. There are some limitations for the SD device drivers. The “Host Controller Register” is not directly accessible by the Secure Digital device drivers.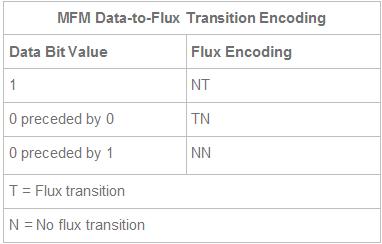

 Flash drives have just changed the lives of students, teachers, businessmen, engineers and other working people for their IT jobs. A flash drive comes up with a lot of features including its light weight, small size, portability, reliability, trustworthiness and large storage ability comparable to the existing removable devices. This is a great external storage device – now you can save even a movie or bulk of files in it which was not possible before in punch cards or later in floppy diskette due to their insufficient space of storage.
Flash drives have just changed the lives of students, teachers, businessmen, engineers and other working people for their IT jobs. A flash drive comes up with a lot of features including its light weight, small size, portability, reliability, trustworthiness and large storage ability comparable to the existing removable devices. This is a great external storage device – now you can save even a movie or bulk of files in it which was not possible before in punch cards or later in floppy diskette due to their insufficient space of storage. 1. Freeware: Undelete Plus
1. Freeware: Undelete Plus Magic Disk
Magic Disk