FreeDOS Update Procedure
 This is a walkthrough on how to upgrade the firmware on a Seagate Serial ATA hard drive.
This is a walkthrough on how to upgrade the firmware on a Seagate Serial ATA hard drive.
(Firmware Update for STM3500320AS, STM3750330AS, STM31000340AS)
Note: For best results during system startup, it is recommended to disconnect peripherals such as USB storage devices, printers, scanners, etc.
If your keyboard does not respond within FreeDOS, use a wired rather than a wireless keyboard.
- Boot up to the CD. Most systems will automatically boot to the CD if it is bootable. If it does not, please consult your system documentation on how to modify the system boot sequence.
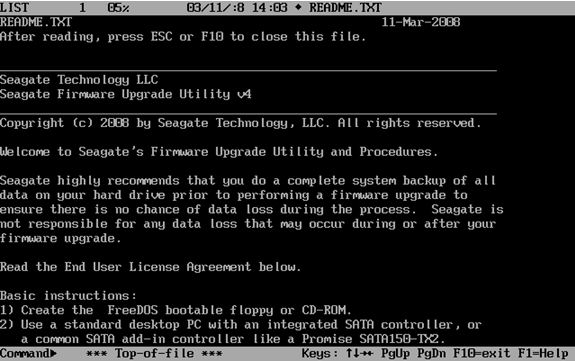
- After the system boots to the CD you will be presented with a README file.

- Press ESC or F10 to proceed to the next step.

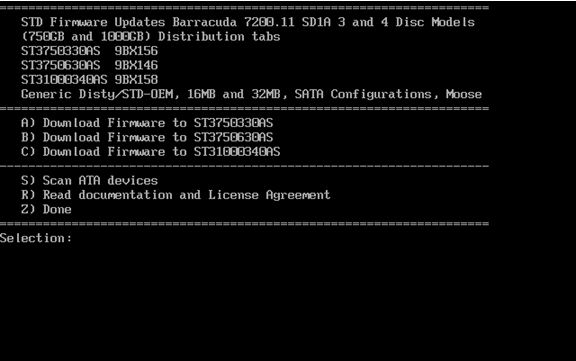
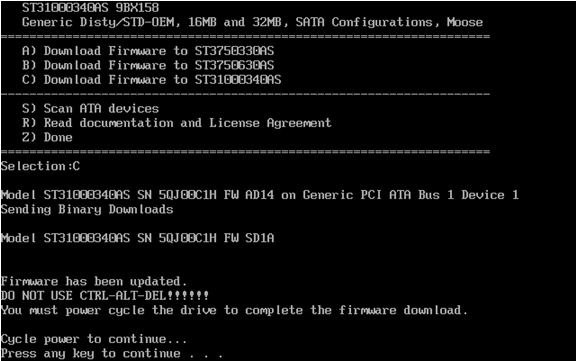
- To select the appropriate drive, press the corresponding key. In this example the letter “C” will start the download for the ST31000340AS. Please note that there are different versions of the firmware for each model of drives.

- Once the firmware update is complete, you will be prompted to turn your computer off by pressing any key.
Note:A soft reset (Control-Alt-Delete) is not sufficient. - Turn on your computer and remove the firmware CD to allow your system to boot normally into your operating system. Your drive has been updated.
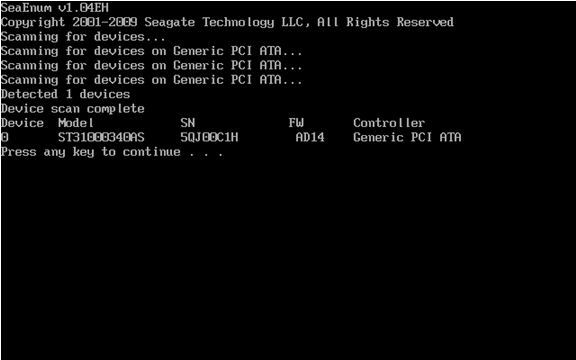
General information: Scanning for devices
You can use the “Scan ATA device” by pressing the “S” key at the “Selection:” prompt to view Seagate drives which are detected.
The scan procedure will display only Seagate drives, and will display the current firmware revision loaded on the drive.

Firmware Update for Macintosh
Can I update the firmware on my hard drive if it is installed in a Mac?
Yes, however it must be an Intel-based Mac (i.e. MacPro and iMac – with Intel inside). There are other models of Macs that have Intel processors such as the MacBook and MacBook Pro notebooks as well as the Mac Mini, but these drives have notebook (2.5 inch) drives which are not affected.
I have a PowerMac. Can I update the firmware on my hard drive?
Older Macs that are PowerPC-based (PowerMac G3, G4, G5 and iMac G3, G4, and G5) are incompatible with the FreeDOS operating system which is required to perform the update.
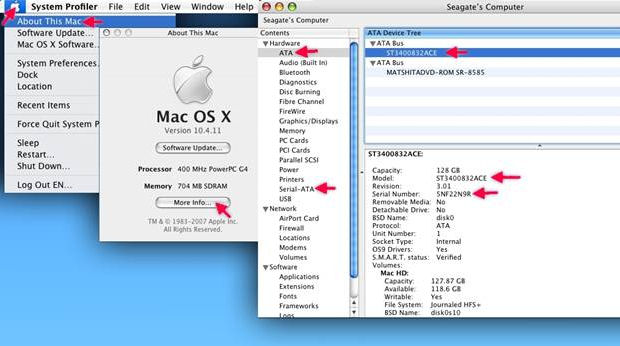
How to find your drive’s serial number and model number in Mac OS X

- Choose the Apple from the menu.
- Choose “About this Mac”
- Choose ” More Info…”
- Choose the drive type: Serial ATA
- Highlight the appropriate drive listed under the bus.
- Below you will see the Model and Serial number of the highlighted drive.
Instructions for updating firmware on an Intel based Mac.
- Download and burn the Firmware ISO that has been provided to you by Seagate for your drive(s)
- Burn the ISO to a CD.
- Insert the freshly burned CD back in to your Mac.
- Reboot
- After the chime, press and hold the Option key on the keyboard.
- Once you see the Apple with the spinning gear beneath, release the Option Key.At this point the system will come to a screen with pictures of hard drives and a CD; the CD should be named Seagate.
- Click on the CD
- Click on the arrow pointing to the right.
- At this point FreeDOS will boot. Follow the on screen instructions.
Firmware Download: FirmwareBase.com