Striped set with dual distributed parity. Provides fault tolerance from two drive failures; array continues to operate with up to two failed drives. This makes larger RAID groups more practical, especially for high availability systems. This becomes increasingly important because large capacity drives lengthen the time needed to recover from the failure of a single drive. Single parity RAID levels are vulnerable to data loss until the failed drive is rebuilt: the larger the drive, the longer the rebuild will take. Dual parity gives time to rebuild the array without the data being at risk if a (single) additional drive fails before the rebuild is complete.
Advantages
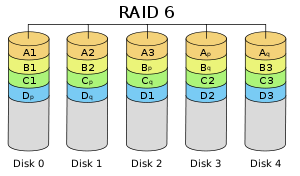
- RAID 6 is essentially an extension of RAID level 5 which allows for additional fault tolerance by using a second independent distributed parity scheme (dual parity).
- Data is striped on a block level across a set of drives, just like in RAID 5, and a second set of parity is calculated and written across all the drives; RAID 6 provides for an extremely high data fault tolerance and can sustain multiple simultaneous drive failures
- RAID 6 protects against multiple bad block failures while non-degraded
- RAID 6 protects against a single bad block failure while operating in a degraded mode
- Perfect solution for mission critical applications
Disadvantages
- More complex controller design
- Controller overhead to compute parity addresses is extremely high
- Write performance can be brought on par with RAID Level 5 by using a custom ASIC for computing Reed-Solomon parity
- Requires N+2 drives to implement because of dual parity scheme
Recommended Applications
- File and Application servers
- Database servers
- Web and E-mail servers
- Intranet servers
- Excellent fault-tolerance with the lowest overhead
RAID 6 VS RAID 5
RAID 6
In complex arrays (12-24 drives), RAID 6 applications would be a preferred choice due to the fact that Serial ATA drives used in the arrays have a lower duty cycle and may be more likely to fail in 24/7 or business-critical applications.
Raid 5
In small arrays (4-12 drives), RAID 5 applications can quickly repair a failed drive and restore lost data-without taking down the array. It’s perhaps the most cost-effective, fault-tolerant data protection solution currently available for small storage devices.
Pro
Raid 6
Designed for tolerating two simultaneous HDD failures by storing two sets of distributed parities.
Raid 5
- Simplified hardware implementation
- A matured industry standard
Con
Raid 6
- For RAID 6, one needs a more complex system with a method for encoding, as well as XOR calculations. For that, one really needs hardware acceleration, otherwise the performance suffers.
- Uses 2 drives for parity
Raid 5
- The risk of simultaneous drive failures grows in proportion to the drive array and can increase if customers purchase all of the disks in an enclosure at one time.
- If the system finds a faulty sector on another drive during this degraded state (one drive down, spare drive being rebuilt), the RAID 5 system would be unable to restore the data onto the spare drive, resulting in data loss.
Recommended Configuration
Raid 6
Disk array consists of 12 disks or more
Raid 5
Disk array consists of 10 disks or less
Recommended Solutions
Raid 6
- Desktop: EnhanceRAID T8
- Rackmount: EnhanceRAID R14; UltraStor RS16
Raid 5
- Desktop: EnhanceRAID T4HCR, T5,T8
- Rackmount: EnhanceRAID R4,R6,R8; UltraStor RS8 or RS2080

