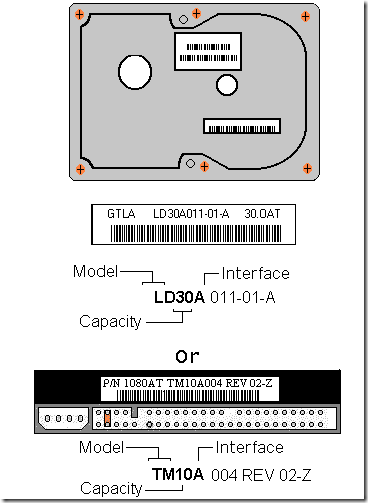
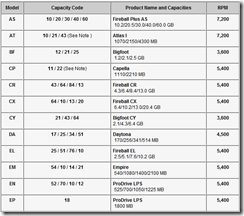
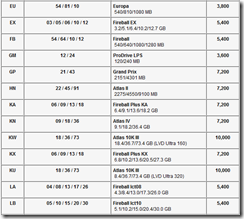
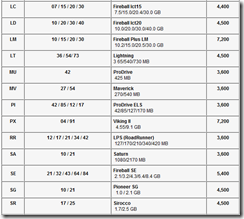
Hard Drive Capacity Measurement Standards
 Discrepancy Between Reported Capacity and Actual Capacity
Discrepancy Between Reported Capacity and Actual Capacity
Many users are confused when their operating system reports, for example, that their new ST31000340AS 1 Terabyte (1000 GB) hard drive is reporting only about 909 Gbytes in “usable capacity“. Several factors may come into play when you see the reported capacity of a disc drive. Unfortunately there are two different number systems which are used to express units of storage capacity;
- Binary – which says that a kilobyte is equal to 1024 bytes
- Decimal – which says that a kilobyte is equal to 1000 bytes.
The storage industry standard is to display capacity in decimal. Even though in binary you have more bytes, the decimal representation of a Gbyte shows greater capacity. In order to accurately understand the true capacity of your disc drive, you need to know which base unit of measure (binary or decimal) is being used to represent capacity. Another factor that can cause misrepresentation of the size of a disc drive is BIOS limitations. Many older BIOS are limited in the number of cylinders they can support.
Motivation for Proposed Prefixes for Binary Multiples
Once upon a time, computer professionals noticed that 1024 or 2 10 (binary) was very nearly equal to 1000 or 10 3 (decimal) and started using the prefix “kilo” to mean 1024. That worked well enough for a decade or two because everybody who talked kilobytes knew that the term implied 1024 bytes. But almost overnight a much more numerous “everybody” bought computers, and the trade computer professionals needed to talk to physicists and engineers and even to ordinary people, most of whom know that a kilometer is 1000 meters and a kilogram is 1000 grams.
Two Different Measurements Systems
| Abbreviation | Binary Power | Binary Value (in Decimal) | Decimal Power | Decimal (Equivalent) |
| Kbyte | 2 10 | 1,024 | 10 3 | 1,000 |
| Mbyte | 2 20 | 1,048,576 | 10 6 | 1,000,000 |
| Gbyte | 2 30 | 1,073,741,824 | 10 9 | 1,000,000,000 |
| Tbyte | 2 40 | 1,099,511,627,776 | 10 12 | 1,000,000,000,000 |
Often when two or more people begin discussing storage capacity, some will refer to binary values and others will refer to decimal values without making distinction between the two. This has caused much confusion in the past. In an effort to dispatch this confusion, all major disc drive manufactures use decimal values when discussing storage capacity.
How Operating Systems Report Drive Capacity?
Windows XP/2000/NT
From Windows Explorer, right click on a drive letter, then click on Properties. This shows capacities in bytes, Mbytes, and Gbytes.
Windows 98/Me
From Windows Explorer, right click on a drive letter, then click on Properties. This shows bytes, Mbytes, and Gbytes.
DOS Prompt ? CHKDSK shows bytes
DOS Prompt ? FDISK shows Mbytes
DOS/Windows 3.x
CHKDSK shows bytes
FDISK shows Mbytes