The goal of this post is to show you how a hard drive Printed Circuit Board(PCB) built. What are its main parts, how do they look and what are these parts names and abbreviations. As an example we are going to disassemble 3.5″ SATA drive.
The goal of this post is to show you how a hard drive Printed Circuit Board(PCB) built. What are its main parts, how do they look and what are these parts names and abbreviations. As an example we are going to disassemble 3.5″ SATA drive.
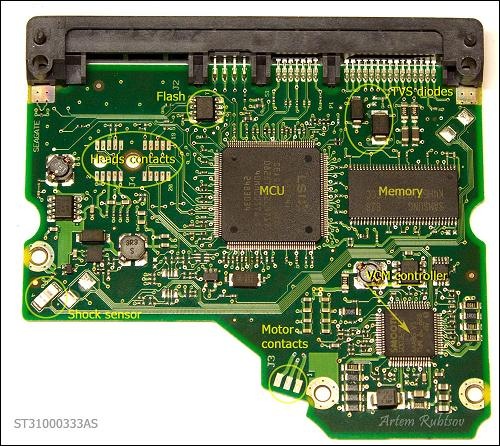
To make it more fun we going to tear to pieces pretty new 1TB Seagate ST31000333AS hard drive. Let’s take a look on our “Guinea pig”.
Hard Drive PCB Main Parts:
The fancy piece of green woven glass and copper with SATA and power connectors called Printed Circuit Board(PCB). PCB holds on place and wires electronic components of HDD.
Now let’s remove PCB and see electronic components on the other side.

Hard Drive PCB Parts:
The heart of PCB is the biggest chip in the middle called Micro Controller Unit(MCU). On modern HDDs MCU usually consists of Central Processor Unit or CPU which makes all calculations and Read/Write channel – special unit which converts analog signals from heads into digital information during read process and encodes digital information into analog signals when drive needs to write. MCU also has IO ports to control everything on PCB and transmit data through SATA interface.
The Memory chip is DDR SDRAM memory type chip. Size of the memory defines size of the cache of HDD. This PCB has Samsung 32MB DDR memory chip which theoretically means HDD has 32MB cache (and you can find such information in data sheet on this HDD) but it’s not quite true. Because memory logically divided on buffer or cache memory and firmware memory. CPU eats some memory to store some firmware modules and as far as we know only Hitachi/IBM drives show real cache size in data sheets for the other drives you can just guess how big is the real cache size.
Next chip is Voice Coil Motor controller(VCM controller). This fellow is the most power consumption chip on PCB. It controls spindle motor rotation and heads movements. The core of VCM controller can stand working temperature of 100C/212F.
Flash chip stores part of the drive’s firmware. When you apply power on a drive, MCU chip reads content of the flash chip into the memory and starts the code. Without such code drive wouldn’t even spin up. Sometimes there is no flash chip on PCB that means content of the flash located inside MCU.
Shock sensor can detect excessive shock applied on a drive and send signal to VCM controller. VCM controller immediately parks heads and sometimes spins down the drive. It theoretically should protect the driver from further damage but practically it doesn’t, so don’t drop you drive – it wouldn’t survive. On some drives shock sensors used for detection even light vibrations and signals from such sensors help VCM controller tune up heads movements. Such drives should have at least two shock sensors.
Another protection device called Transient Voltage Suppression diode(TVS diode). It protects PCB from power surges from external power supply. When TVS diode detects power surge it fries itself and creates short circuit between power connector and ground. There are two TVS diodes on this PCB for 5V and 12V protection.
Tips: Hard Drive Failures cased by PCB can be solved by replacing a new one. How to find a matching pcb please refer to: How to find a Matching PCB